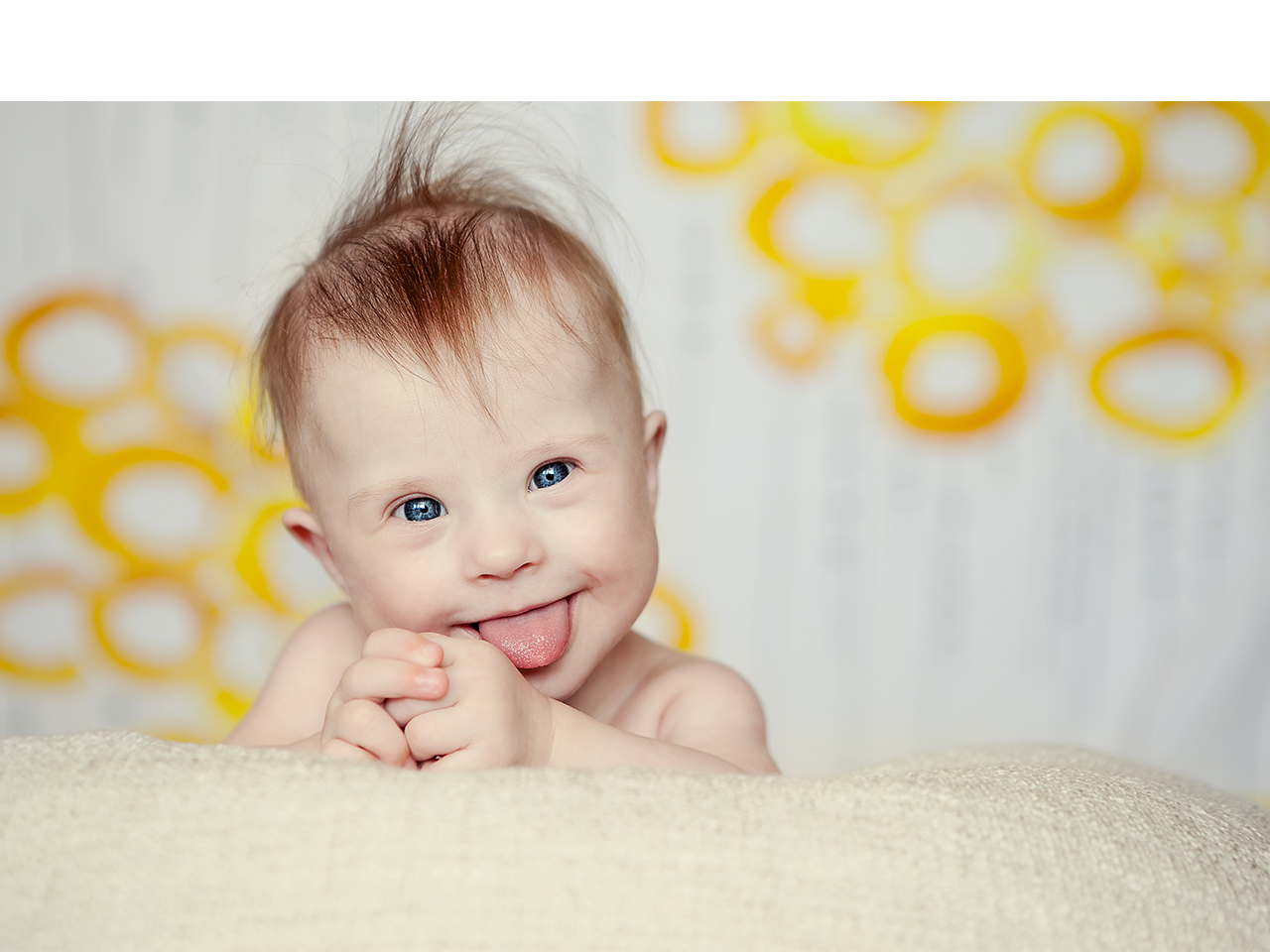
We have seen numerous kids with a disorder commonly known as The Down Syndrome. These children are considered “special kids” because they are born with certain deformities or disabilities that makes them different than other children. Such kids should never be neglected or treated differently in fact, they have all the more reasons to be loved and cared for. But have you wondered what causes such deformity in these children? What is the root cause of it call. Why hasn’t science come up with a way to treat this disorder in kids? And most of all, what do the parents of these children feel like and how do they deal with them? We have answered all your questions down below.
The Down Syndrome (DS), additionally called Trisomy 21, is a condition where someone is born with an additional chromosome. Chromosomes contain hundreds, or even thousands, of qualities. Qualities convey the data that decides your attributes (highlights or attributes gave to you from your folks). With Down condition, the additional chromosome causes delays in the manner in which a kid grows, intellectually, and even physically.
The physical highlights and clinical issues related to Down condition can fluctuate broadly from kid to kid. While a few children with DS need a ton of clinical consideration, others have relatively healthier lives.
Despite the fact that Down disorder can’t be forestalled, it very well may be identified before a baby is conceived. The medical issues that may oblige DS can be dealt with, and numerous assets are accessible to help kids and their families who are living with the condition.
Typically, when being conceived, a fetus acquires hereditary data from its parents as 46 chromosomes: 23 from the mother and 23 baby gets an additional chromosome 21 — for a sum of 47 chromosomes rather than 46. It’s this extra hereditary material that causes the physical highlights and formative deferrals related to DS.
Albeit nobody knows without a doubt why DS occurs and it is extremely unlikely to forestall the chromosomal blunder that causes it, researchers do realize that ladies of age over 35 have an essentially higher danger of having a kid with the condition. At age 30, for instance, a lady has around a 1 out of 1,000 possibilities of having a baby with DS. Those chances increment to around 1 out of 400 by age 35. By 40 the hazard ascends to around 1 out of 100.
Children with Down condition will in general offer certain physical highlights, for example, a level facial structure, an upward inclination to the eyes, little ears, and a jutting tongue.
Low muscle tone (called hypotonia) is additionally normal for youngsters with DS, and infants specifically may appear to be particularly “floppy.” Though this can and regularly improve after some time, most kids with DS ordinarily arrive at formative achievements — like sitting up, creeping, and strolling — later than different children.
During childbirth, kids with DS are ordinarily of normal size, however, they will, in general, develop at a more slow rate and stay littler than their companions. For newborn children, low muscle tone may add to sucking and taking care of issues, just as stoppage and other stomach related problems. Babies and more established children may have delays in discourse and self-care aptitudes like taking care of, dressing and latrine educating.
Down condition influences children’s capacity to learn in various manners, however, most have gentle to direct scholarly impedance. Children with DS can and do learn, and are fit for creating abilities for the duration of their lives. They just arrive at objectives at an alternate pace — which is the reason it’s significant not to contrast a kid and DS against ordinarily creating kin or many other kids with the condition.
Children with DS have a wide scope of capacities, and it is highly unlikely to tell during childbirth what they will be fit for as they grow up.
While a few children with DS have no apparent medical issues, others may encounter a large group of clinical issues that require additional consideration. For instance, practically 50% of all kids brought into the world with DS will have an inherent heart deformity.
Children with Down disorder are likewise at an expanded danger of creating pneumonic hypertension, a genuine condition that can prompt irreversible harm to the lungs. All newborn children with Down condition ought to be assessed by a pediatric cardiologist.
Roughly 50% of all children with DS likewise have issues with hearing and vision. Hearing misfortune can be identified with liquid development in the inward ear or to basic issues of the ear itself. Vision issues usually incorporate strabismus (cross-looked at), close or farsightedness, and an expanded danger of waterfalls.
Normal assessments by an otolaryngologist (ear, nose, and throat specialist), audiologist, and ophthalmologist are important to identify and address any issues before they influence language and learning abilities.
Other ailments that may happen all the more every now and again in kids with DS incorporate thyroid issues, stomach, and intestinal issues, seizure issues, breathing issues, including rest apnea and asthma, stoutness, an expanded possibility of contaminations, and a higher danger of youth leukemia. Individuals with Down disorder now and then have a flimsy upper spine and ought to be assessed by a specialist before taking an interest in physical exercises. Luckily, a large number of these conditions are treatable.
Two kinds of pre-birth tests are utilized to distinguish Down disorder in a hatchling: screening tests and demonstrative tests. Screening tests gauge the hazard that an embryo has DS; analytic tests can tell whether the baby really has the condition.
Screening tests are financially savvy and simple to perform. But since they can’t offer a complete response with regards to whether a child has DS, these tests are utilized to assist guardians with concluding whether to have progressively analytic tests.
Symptomatic tests are about 99% exact in recognizing Down condition and other chromosomal anomalies. Be that as it may, in light of the fact that they’re performed inside the uterus, they are related with a danger of premature delivery and different complexities.
Therefore, intrusive analytic testing recently was commonly suggested distinctly for ladies age 35 or more established, those with a family ancestry of hereditary imperfections, or those who’ve had a strange outcome on a screening test.
In any case, the American College of Obstetrics and Gynecology (ACOG) presently suggests that every single pregnant lady be offered screening with the alternative for obtrusive analytic testing for Down disorder, paying little mind to age.
In case you’re uncertain about which test, assuming any, is directly for you, your primary care physician or a hereditary advocate can assist you with figuring out the upsides and downsides of each.
Screening tests include:
Nuchal translucency testing. This test, performed somewhere in the range of 11 and 14 weeks of pregnancy, utilizes ultrasound to gauge the away from in the folds of tissue behind a building up infant’s neck. (Children with DS and other chromosomal variations from the norm will in general amass liquid there, causing the space to seem bigger.) This estimation, taken along with the mother’s age and the infant’s gestational age, can be utilized to ascertain the chances that the infant has DS. Nuchal translucency testing is normally performed alongside a maternal blood test.
The triple screen or fourfold screen (likewise called the different marker test). These tests measure the amounts of ordinary substances in the mother’s blood. As the names infer, triple screen tests for three markers; the fourfold screen incorporates one extra marker and is progressively precise. These tests are commonly offered somewhere in the range of 15 and 18 weeks of pregnancy.
Incorporated screen. This uses results from first-trimester screening tests (with or without nuchal translucency) and blood tests with a subsequent trimester fourfold screen to concoct the most exact screening results.
A hereditary ultrasound. A point by point ultrasound is regularly performed at 18 to 20 weeks related to the blood tests, and it checks the baby for a portion of the physical characteristics irregularities related to Down condition.
Cell-free DNA. This test dissects fetal DNA found in the mother’s blood. It tends to be done in the first trimester and is more exact at recognizing Trisomy 21 than standard blood tests. Right now cell-free DNA testing is just offered to ladies at high danger of having a child with Down Syndrome.
Analytic tests include:
Chorionic villus examining (CVS). CVS includes taking a minuscule example of the placenta, either through the cervix or through a needle embedded in the mid-region. The benefit of this test is that it very well may be performed during the main trimester, commonly somewhere in the range of 10 and 12 weeks. The drawback is that it conveys a marginally more serious danger of unnatural birth cycle as contrasted and amniocentesis and has different intricacies.
Amniocentesis. This test performed somewhere in the range of 15 and 20 weeks of pregnancy, includes the expulsion of a limited quantity of amniotic liquid through a needle embedded in the midsection. The cells would then be able to be broke down for the nearness of chromosomal variations from the norm. Amniocentesis conveys a little danger of inconveniences, for example, preterm work and unnatural birth cycle.
Percutaneous umbilical blood testing (PUBS) or cordocentesis. Typically performed following 18 weeks, this test utilizes a needle to recover a little example of blood from the umbilical line. It conveys dangers like those related to amniocentesis.
After an infant is conceived, if the specialist presumes DS dependent on the newborn child’s physical attributes, a karyotype — a blood or tissue test recolored to show chromosomes gathered by size, number, and shape — should be possible to confirm the conclusion.
In case you’re the parent of a baby determined to have Down disorder, you may from the start feel overpowered by sentiments of misfortune, blame, and dread. Chatting with different guardians of children with DS may assist you with managing the underlying stun and pain and discover approaches to look toward what’s to come. Numerous guardians find that learning as much as possible about DS helps facilitate a portion of their feelings of dread.
Specialists suggest enlisting kids with Down disorder in early-mediation benefits as quickly as time permits. Physical, word related, and language instructors and youth teachers can work with your kid to support and quicken advancement.
Where to send your DS child to class can be a troublesome choice. A few children with Down disorder have needs that are best met in a particular program, while numerous others do well-going to neighborhood schools close by peers who don’t have DS. Studies have demonstrated that this sort of circumstance, known as consideration, is useful for both the kid with DS just as different children.
Your school locale’s kid study group can work with you to figure out what’s best for your kid, yet recollect, any choices can and ought to include your contribution, as you are your kid’s best supporter.
Today, numerous children with Down condition go to class and appreciate a significant number of indistinguishable exercises from different children their age. A couple goes on to school. Many changes to semi-free living. Still, others keep on living at home yet can hold occupations, along these lines finding their own achievement in the network.